The volatile crypto markets have continued to capture the imagination of the financial world. The rapid price actions have presented a range of opportunities when it comes to cryptocurrency arbitrage and trading. Unlike the traditional financial market where the final frontier may have already been explored when it comes to advanced trading functionality, the crypto space is far less efficient. Opportunities for arbitrage exist around every corner – but how do we take advantage of these opportunities?
This article will focus on a few of the most simple arbitrage opportunities available in the market. Upon completion of this article, you will not only better understand how arbitrage works in the cryptocurrency market, but you will be provided the tools to execute an arbitrage strategy of your own.
What is crypto arbitrage?
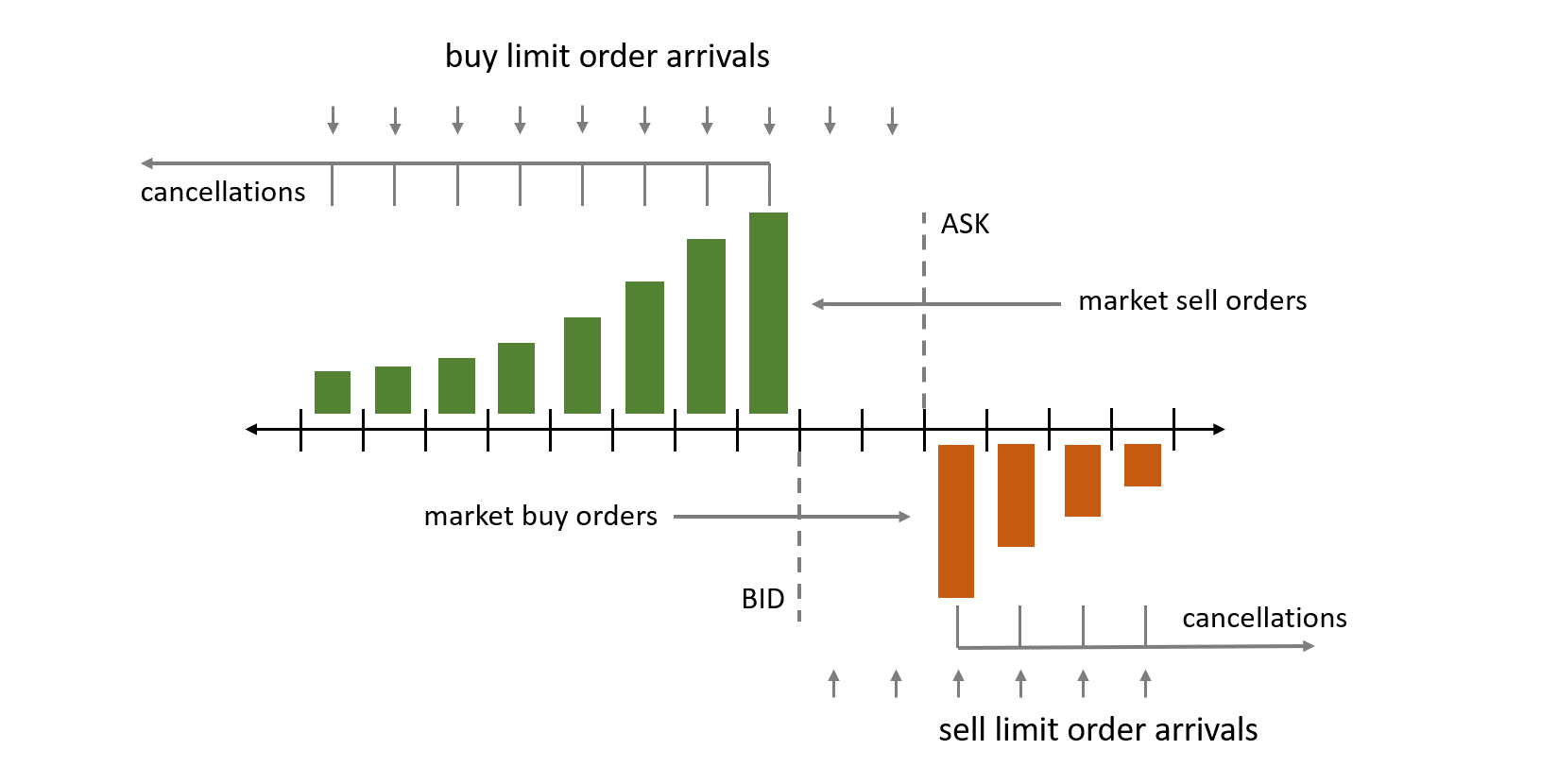
Arbitrage is the process of taking advantage of inefficiencies in markets. In the case of cryptocurrencies, this can occur as the price of assets fluctuates over time. If there is a difference between the price of an asset across exchanges (or even potentially within the same exchange), it may be possible to buy and sell the same asset in a way which will result in a net profit.
This process will be dissected in more detail throughout the remainder of this article. We will discuss how to calculate arbitrage opportunities, how to take advantage of these situations, and even how to build your own trading system designed for arbitraging the market
How is an arbitrage opportunity calculated?
The arbitrage opportunity for any market is calculated by identifying the overlap between the highest bid prices and the lowest ask prices. When the bid price on one exchange is higher than the ask price on another exchange for a cryptocurrency, this is an arbitrage opportunity.
Now, before we start throwing trades at this situation hoping for a quick buck, let’s take a measured approach by calculating the size of the opportunity. One thing we need to remember when calculating the value of the arbitrage opportunity: Executing the arbitrage will result in consuming the order book. For example, let’s look at “Step 2” in the illustration to the left. In this step, we have highlighted the amount of the order book which overlaps. That means the bid price on one exchange is higher or equal to the ask price on another exchange for the highlighted area.
However, once we begin executing on the arbitrage opportunity, what we notice in steps 4 and 5 is that consuming the order book results in the arbitrage opportunity shrinking after each price value is taken. Therefore, we aren’t able to capitalize on all of the value which is highlighted in yellow in step 2 (the area of the depth), but only a fraction of the value.
When calculating the size of the opportunity, we must therefore take this behavior into account. We can do this by systematically simulating the execution of the actual buys and sells we would actually make on the exchange during the arbitrage.

How are trades executed to take advantage of the arbitrage opportunity?
Now that we understand conceptually how arbitrage happens, let’s discuss the most popular types of arbitrage opportunities: Simple and Triangular Arbitrage.
Simple Arbitrage
Simple arbitrage is the buying and selling action we described in our previous examples in this article. Simple arbitrage buys and sells the same crypto asset on different exchanges as quickly as possible to take advantage of the inefficiencies of pricing across exchanges.
This form of arbitrage does not require any additional trades outside those necessary to swap the two assets which are shared by the asset pair which is exhibiting the arbitrage opportunity.
Triangular Arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage is an event which can occur on a single exchange (or across multiple exchanges) where the price differences between three difference cryptocurrencies leads to an arbitrage opportunity. Since many exchanges have a number of markets with a variety of quote currency options. This opens up a long list of triangular trading patterns which can be leveraged to take advantage of inefficiencies in an individual exchanges pricing.

Begin at one asset. This asset will be the asset to which we eventually return after completing the arbitrage loop.
Trade to a second currency which connects to both the original asset and the next asset in the loop. This is required to prevent transversing on the same path.
Trade to a third currency which connects both the first and second asset. This second trade locks in a zero-risk profit due to the rate inconsistencies across the 3 pairs.
Convert the third currency back for the original asset.
In the illustrated example, we begin with a value of 1.0000 BTC. To calculate the value of the opportunity, go around the triangle and calculate the bid and ask prices for each trading pair. Note that the bottom trade uses the ask price and we divided ETH by LTC in order to calculate the ratio. Once each of these values has been calculated, we simply go around the triangle and multiple or divide based on the operation that is dictated in the illustration. This would look like the following:
1.00000 x 138.23611 ÷ 2.52871 x 0.01894 = 1.03539 BTC
Arriving back at BTC, we can compare the end value to our starting value to determine the size of the opportunity. As we can see in this example, the end value was 1.03539 BTC. If we compare this to the starting value of 1.00000 BTC, we find the value of this opportunity is 0.03539 BTC. That means just by executing on this arbitrage opportunity, we increase our BTC holdings.
Note: Triangular arbitrage can be performed across multiple exchanges, but we won’t touch on those strategies in this article.
Putting it all together
Now that we know how to find and quantify arbitrage opportunities, we can pull everything together to complete our strategy.

First – Fund Exchange Accounts
Place funds on two different exchanges which will be monitored for arbitrage opportunities. These funds will be used to execute a simple arbitrage where the same asset is bought and sold instantaneously when an opportunity arises. Ideally, you would want to have funds on multiple exchanges since the process to transfer funds from one exchange to another is time consuming and can become expensive. Not to mention, it’s easiest to strike at opportunities the split second they happen.
Second – Identify Opportunities
Identify opportunities by looking for a difference in pricing across exchanges. Compare the highest bid prices to the lowest ask prices to see where these values overlap. Anything which is overlapping is a potential arbitrage opportunity.
Third – Quantify Opportunities
Calculate the value of the opportunity by systematically simulating the selling and buying of the asset. This process will consume the order book, so make sure to take this aspect into account.
Fourth – Execute the Strategy
Execute the strategy by instantly placing orders with the exchange. Continue to place orders with the exchange to take advantage of the arbitrage opportunity as long as the opportunity is available.
Fifth – Do It Again
Stop once the opportunity is no longer available. At this time, it’s time to start looking for a new opportunity to do it all over again.
Enjoy the profits!







This Post Has 5 Comments
Great post! How would this calaulation change to take into account transaction fees? Thanks
Hi Chris
It is calculated based on the exchange rate at the time.
I don’t get the simple arbitrage. We keep BTC funds in 2 different exchange and let’s say there is enough gap for BTC/USDT pair in those exchanges. We need buy in one of them and sell it on another. Let’s say we bought USDT in one exchange how can we sell this on another one without transferring the fund to the other one? Our fund in the other exchange is still in BTC. But we have to sell USDT and get BTC and we don’t have USDT in the other exchange.
Thanks for asking! The way you can do this is by holding funds on both exchanges. I can provide a brief example here using two different exchanges.
Let’s say you have two exchange accounts. One on Coinbase and one on Kraken. For this example, we want to trade between BTC/USD when there are arbitrage opportunities. The way you can do this is by holding $1,000 USD on Kraken and 0.1 BTC on Coinbase. When the arbitrage opportunity arises, you would sell the USD on Kraken to buy Bitcoin and sell the BTC on Coinbase to buy USD.
The result would be that you have USD on Coinbase now and BTC on Kraken. If the arbitrage was successful, you would have more funds than you did before the trade. So, now you might have $1,050 and 0.1 BTC.
Please let me know if this helps answer your question!
Thanks for asking! The way you can do this is by holding funds on both exchanges. I can provide a brief example here using two different exchanges.
Let’s say you have two exchange accounts. One on Coinbase and one on Kraken. For this example, we want to trade between BTC/USD when there are arbitrage opportunities. The way you can do this is by holding $1,000 USD on Kraken and 0.1 BTC on Coinbase. When the arbitrage opportunity arises, you would sell the USD on Kraken to buy Bitcoin and sell the BTC on Coinbase to buy USD.
The result would be that you have USD on Coinbase now and BTC on Kraken. If the arbitrage was successful, you would have more funds than you did before the trade. So, now you might have $1,050 and 0.1 BTC.
Please let me know if this helps answer your question!