Trading cryptocurrency can be confusing. Even the smallest details can make a big difference when executing a trade. The small detail we will focus on for this article is the market spread.
Some of the questions we will answer throughout this article include:
What is the market spread?
How do we calculate the market spread?
How does the market spread impact our trading strategy?
What is market spread?
The market spread is the gap between the highest bid offer and the lowest ask offer on the order book. The gap is essentially the difference between the price at which people are willing to sell an asset and the price that other people are willing to buy an asset.
Simplifying it even further, imagine you are negotiating a deal to buy Bitcoin from someone. You might tell the other person you are willing to buy one Bitcoin for $5,000. However, the other person might respond to your offer by saying they think it’s worth more than $5,000, so they are willing to sell it for $7,000.
The difference between your bid to buy Bitcoin for $5,000 and the other person’s ask to sell Bitcoin for $7,000 is the spread.
Extrapolating this situation to a cryptocurrency exchange, the order book is essentially hundreds or even thousands of people saying what price they are willing to buy or sell an asset (like Bitcoin). The people with the lowest asking price and the highest bid price are on either side of the market spread.
How do we calculate the market spread?

Now that we better understand the concept of the market spread, we can discuss how the market spread is calculated.
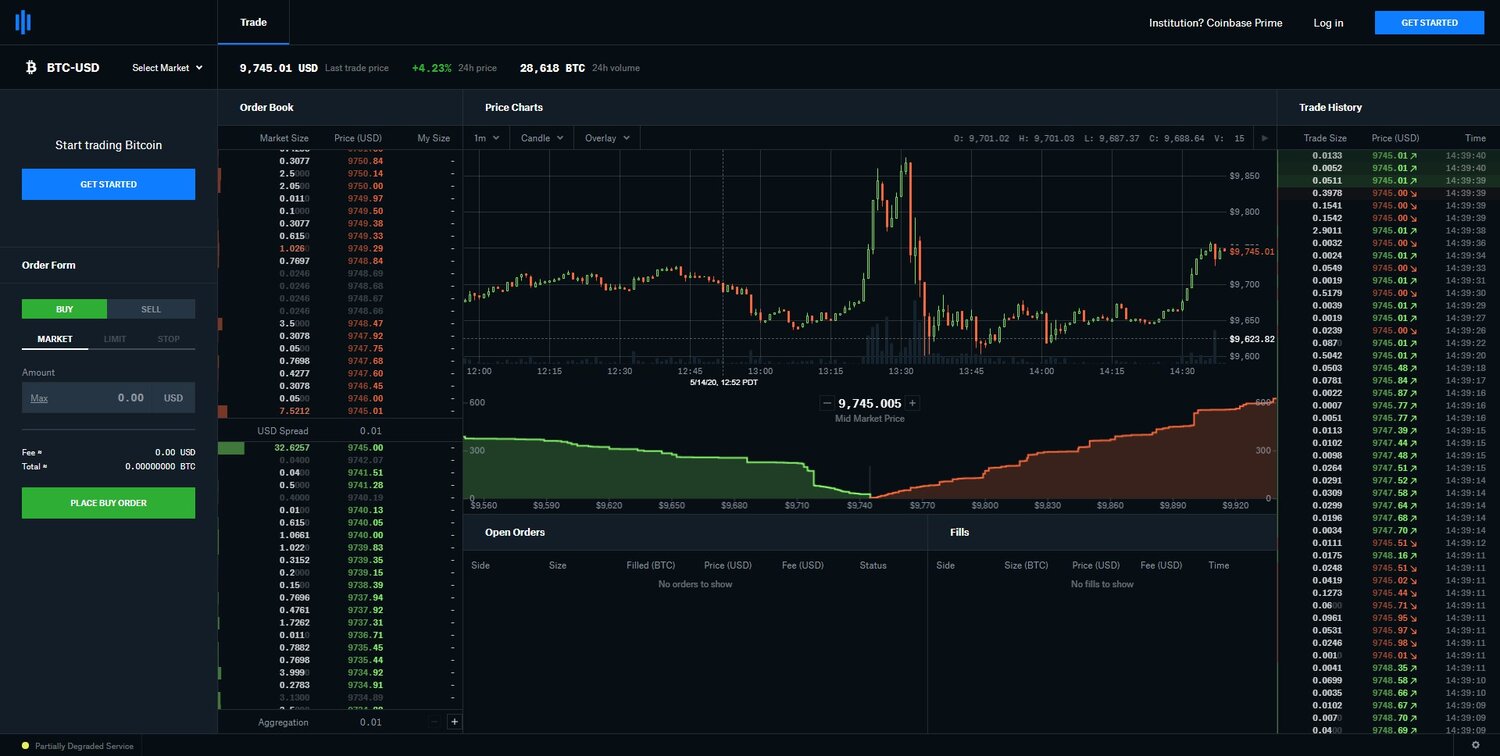
In the image to the right, we can see the best bids and asks on the Coinbase Pro exchange for the BTC/USD trading pair at one moment in time.
We can see the lowest ask price for Bitcoin was $9745.01 and the highest bid price for Bitcoin was $9745.00. To calculate the spread, all we need to do is subtract the highest bid price from the lowest ask price.
AL – BH = Spread
where,
AL is the lowest ask price
BH is the highest bid price
Spread = $9745.01 – $9745.00 = $0.01
Notice that for the trading pair BTC / USD the quote currency is USD and the base currency is BTC. Since USD is the quote currency, the price values will be in terms of US Dollars. Not all markets will be in terms of US Dollars since other currencies, like Bitcoin, can also be quote currencies. In that case, the prices will be terms of the other quote currency.
Besides knowing the raw value of the spread, it’s also possible you will want to know the percent spread. The percent spread can be useful in determining the liquidity of the market.
Percent Spread = (S / AL) x 100
where,
S is the spread
AL is the lowest ask price
Multiple by 100 to convert from decimal to percent
Percent Spread = (0.01 / 9745.01) x 100 = 0.0001%
How does the market spread impact a trading strategy?
The market spread can play a powerful role in the performance of your trading strategy. At first thought, many traders will only consider the influence of the trading fee on their performance. After deeper thought, some traders will come to the realization that the market spread can actually impact performance far greater than the trading fee.
When executing a strategy that trades frequently, we must take into consideration the influence of the market spread to ensure our strategy is profitable. Unfortunately, many backtesting tools in the market fall into the trap of not considering the market spread when simulating trades. These inaccuracies lead to dramatic differences between the simulated data and reality.
Let’s look at an example of how the market spread impacts trades.
Say the current highest bid offer for Bitcoin is $7,500.00 and the lowest ask offer is $8,000.00. In this case, the spread would be exactly $500.00. Using our nifty percent spread equation, we would also see the percent spread is 6.25%. That’s pretty significant.
If we were to buy Bitcoin at the $8,000.00 price (since it’s the lowest ask offer available), we wouldn’t be able to turn a profit when we sold Bitcoin until the best bid price increased to over $8,000.00 (not including trading fees). That would mean the bid price would need to rise substantially just to receive a profit. In the illustration , we can see that even though the price of Bitcoin rose by $300 we still lost money in this trade because we bought Bitcoin for $8,000.00 and then had to sell it at $7,800.00 due to the large spread.

In another case, say the current highest bid offer for Bitcoin was $7,500.00 and the lowest ask offer was $7,501.00. The percent spread in this situation is only 0.013%. Not only is that a tight spread, but we would only need to have the bid price rise by $1 in order to turn a profit (ignoring the cost for trading fees).
Going back and forth over a large spread quickly can be costly. When making a trade, we must take into consideration the cost of the spread so we don’t lose money. Conceptually, it’s far easier to turn a profit on an asset with a small spread than one with a large spread since the asset performance needs to be higher when the spread is larger.